
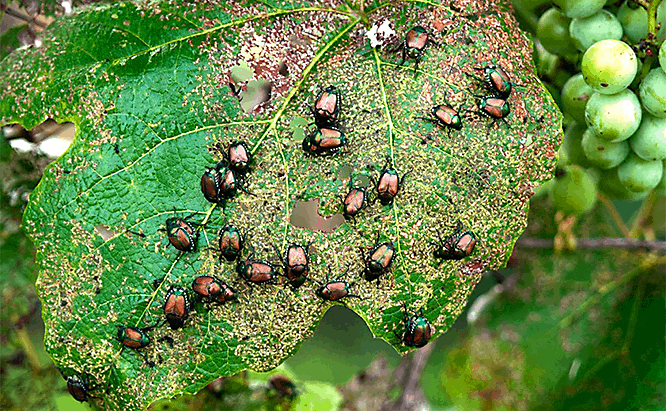
Japanese Beetles
Japanese Beetles may be small, but they come with a large threat. They don’t discriminate: they will eat any type of plant. They are a pest to hundreds of species, and a major pest throughout Michigan. Before the beetle was introduced to the US, it was only found in Japan. It was isolated by water; thus, its natural enemies were able to keep it in check.
How To Identify Japanese Beetles
They are around a half inch long, they have tan wings, metallic blue heads, copper backs, and on their abdomen, they have small white hairs. They generally feed in a small group. They lay their eggs during June, in the soil. They develop for 10 months and then grow in the soil.
They don’t emerge from the soil until they are adults. Despite the fact that their life cycle is just 40 days, they cover a lot of ground.
Japanese Beetle Damage
They will eat a wide variety of crops and flowers, attacking over 300 types of plants. They are particularly keen on raspberries, roses, grapes, and beans. They attack the majority of the foliage, leaving skeletonized leaves. Be sure that you identify them by their appearance, though, as Mexican Bean Beetles also leave leaves skeletonized.
Japanese Beetle Control
Japanese Beetles will eat plants and also are the source of the grubs that are found in your lawn. It is important to control the amount of Japanese beetles on your property. Our perimeter pest control program will help keep the population of Japanese beetles down. Plans start as low as $150 per year.
Japanese Beetle Grub Control
Grubs chew off grass roots which stress the grass roots because the grass is not able to get enough water through its roots. This results in large patches if grass dieing and new grass will have to be planted in these areas. There is a way to prevent grub damage! Sign up for a preventative grub control plan and you will not have to worry about grubs destroying your lawn. The grub control preventative needs to be put down by mid-June because else it will be too late to kill the grubs.